- Home > Travel > About Qufu
Qufu Introduction
Located in southwestern Shandong and covering an area of 815 km² , as the hometown of Confucius, the great thinker, statesman, educator and founder of Confucianism in ancient China, Qufu is a world famous historical and cultural city, which is called one of the World's Three Holy Cities together with Jerusalem and Mecca.

Confucian Temple(孔庙)
Qufu Confucian Temple, the place offering sacrifice to Confucius and demonstrating Confucianism, was founded in Zhou Dynasty(1046-265BC) and completed in Ming(1368-1644AD) and Qing Dynasties(1636-1912AD). It is the largest one among more than 2000 Confucian temples in the world.
Having a three-way layout, the Temple now occupies an area of 140,000 square meters, with nine courtyards running through a central axis and symmetrically arranged left and right. The whole architectural complex includes totally 466 buildings including five halls, one pavilion, one altar, two lobbies and 17 stele pavilions, respectively built in the period of Jin(1115-1234 AD), Yuan(1271—1368 AD), Ming, Qing and Republic of China(1912-1949 AD). The Dacheng Hall, which is the main building, has the roof of double eave and gable with yellow tiles and cornices. It is one of the Three Oriental Halls.Inside the temple, there are more than 1040 inscriptions of successive dynasties since Han Dynasty, together with a large number of precious cultural relics such as books, paintings, doorplates and plaques.
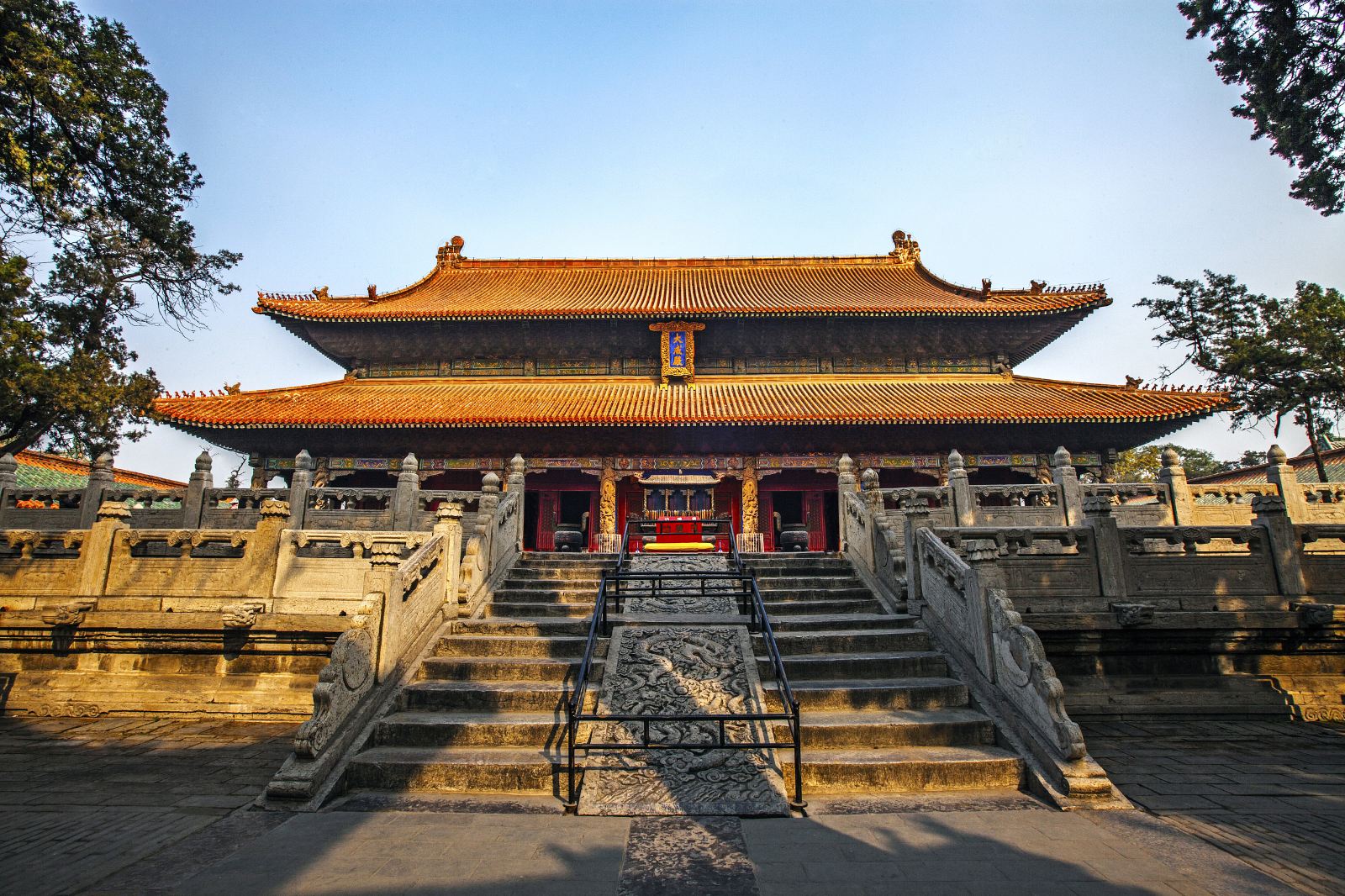
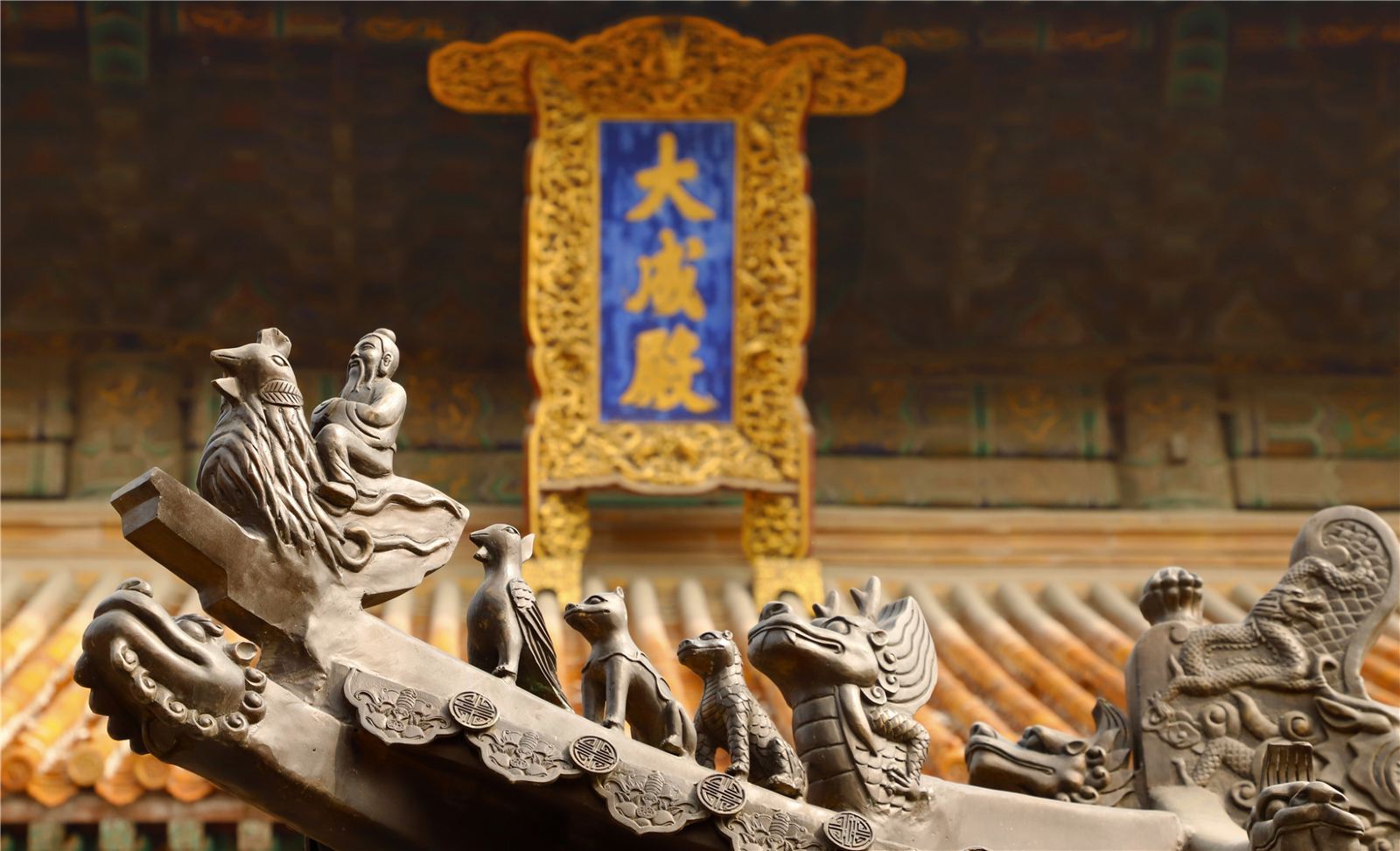


Confucian Mansion(孔府)
Confucian Mansion, where the eldest lineal grandson of Confucius lived, is the most ancient and best preserved surviving architectural complex of the largest scale in China. It combines official and residential function, and is known as “The First Household Under Heaven”.
After the death of Confucius and before the Song Dynasty, the eldest son and grandson lived in the old Queli residence next to the Confucian Temple, and took care of the relics of Confucius and worshiped him. The place they lived became“the residence of descendant with the inherited title”. While respecting Confucius and promoting Confucianism, emperors of all dynasties added officials and titles to Confucius’ descendants and granted land to build residence. During the Baoyuan period of the Song dynasty, Kong Zongyuan, Confucius’ grandson of the forty-six generation, was titled of “Lord YanSheng” and the magistrate of Qufu. New mansion was built, which was renamed the Mansion of Lord YanSheng.Lords Yansheng of all generations, abiding by the ancestral precept of "handing down the poetry and the rites”, were dedicated to collecting ritual utensils and legacies from past dynasties. More than 100,000 items were collected, especially the portraits of Confucius, Lords Yan Sheng and their wives, along with the hats and clothes of Yuan and Ming Dynasties. The most famous collections of Confucian Mansion are also the documents and archives of Ming and Qing Dynasties, which are the real records of various activities of Confucian Mansion for more than 400 years, with a total of over 300,000 pieces. They are the most numerous and oldest private files in China.

Confucian Cemetery(孔林)
As a family cemetery, Confucian Cemetery is one of the greatest in the world. Since Confucius be “buried in the north of Lu city near Sishui river”, his descendants of more than two thousand years were buried nearby uninterruptedly. With more than 100,000 burial mounds, the Cemetery has become the largest family one lasted the longest time in the world.
After Confucius’ death, “his disciples planted all kinds of rare trees around the cemetery, so many different kinds that no one in Lu city could recognize for generations. The Cemetery, which is currently 2 million square meters, are covered by more than 100,000 trees, including 9,000 ancient and famous trees over 200 years old. As having also more than 130 kinds of exotic flowers and grasses in addition, it could be said that the Cemetery is a natural botanical garden.
With more than 4,000 tombstones from Jin, Yuan, Ming and Qing Dynasties to the Republic of China, the Cemetery is also an open-air museum integrating tombs, architecture, stone carvings, and inscriptions. Besides the Han steles moved into the Confucian temple, there are also inscriptions written by famous calligraphers such as Li Dongyang, Yan Song, Weng Fanggang, and Kang Youwei.
The Major Scenic Spots include the residential area, the Well in the Rough Alley and the Fusheng Hall. Yan Temple is now a national key cultural relics protection unit.
Zhougong Temple(周公庙)
Zhougong Temple (the Temple of Duke Zhou), is the former Taimiao of the State of Lu. Taimiao is supposed to be the ancestral temple of the emperor. As Duke Zhou was only a vassal of the Zhou Dynasty, not the emperor, the Zhougong Temple should not have been called Taimiao. But Duke Zhou was with great achievements for creating rites and music, therefore King Cheng of Zhou specially authorized the State of Lu(Duke Zhou’s territory)to sacrifice the former emperor. As a result, the rites and music belonged to the emperor were practiced in the State of Lu. King Cheng ordered the Lu State to set up the Taimiao Temple after Duke Zhou's death.
After Confucius’ death, “his disciples planted all kinds of rare trees around the cemetery, so many different kinds that no one in Lu city could recognize for generations. The Cemetery, which is currently 2 million square meters, are covered by more than 100,000 trees, including 9,000 ancient and famous trees over 200 years old. As having also more than 130 kinds of exotic flowers and grasses in addition, it could be said that the Cemetery is a natural botanical garden.
With more than 4,000 tombstones from Jin, Yuan, Ming and Qing Dynasties to the Republic of China, the Cemetery is also an open-air museum integrating tombs, architecture, stone carvings, and inscriptions. Besides the Han steles moved into the Confucian temple, there are also inscriptions written by famous calligraphers such as Li Dongyang, Yan Song, Weng Fanggang, and Kang Youwei.

Nishan Confucian Temple and Nishan Academy(尼山孔庙&尼山书院)
Nishan Confucian Temple is located at the east foot of Nishan about 28 kilometers southeast of Qufu City.
The original name of Nishan Mountain is Niqiu Mountain. To avoid the taboo of Confucius, whose name in Chinese is Qiu, the moutain is renamed as Nishan. The mountain is not tall, about 340 meters above sea level, with beautiful scenery.
As the Chinese saying goes,“Mountains are famous for living saints and waters gains miraculous for residing dragons.”Nishan is famous at home and abroad because Confucius, the great Chinese thinker, statesman and educator, was born here. The Nishan Confucian Temple is close to Nishan on the back, Yishui River in the East, and faces the village of Yanhui’s mother across the water. Nishan architectural complex is composed of temples in front and an academy in the back, each of which is an independent area. Having five courtyards and three routes layout, the temple covers an area of about 23 acres, with 27 buildings, 69 rooms and a construction area of 1700 square meters. In front of the temple is Zhiyuan River, across which a bridge is built.
In 2006, Nishan Mountain was announced as a national key cultural relics protection unit, and Nishan Confucian Temple and Academy were also listed as the expansion projects of the world cultural heritage of “Three Kong&rdquo.
Yan Temple(颜庙)
Yan Temple, also known as Fusheng temple, is a temple to worship Yan Hui, who is honored as Fusheng ( which means “another holy sage after Confucius”). Yan Hui, styled himself as Ziyuan, is a disciple of Confucius, known for his virtue, poor but studious, admired by later generations.
According to the records of “Rough Alley Annals”, the construction of the temple on the former site of Yan Hui in the Rough Alley started when Emperor Gaozu of Han Dynasty visited Shandong Province and sacrificed Confucius and Yan Hui simultaneously. Rebuilt and expanded in the following dynasties of Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming and Qing Dynasties, the area reached 85 acres with five courtyards in the 22nd year of Wanli Period of Ming. There are 159 halls and pavilions, which are divided into the East, the Middle and the West. The main buildings are all built in the Yuan Dynasty.The original name of Nishan Mountain is Niqiu Mountain. To avoid the taboo of Confucius, whose name in Chinese is Qiu, the moutain is renamed as Nishan. The mountain is not tall, about 340 meters above sea level, with beautiful scenery.
As the Chinese saying goes,“Mountains are famous for living saints and waters gains miraculous for residing dragons.”Nishan is famous at home and abroad because Confucius, the great Chinese thinker, statesman and educator, was born here. The Nishan Confucian Temple is close to Nishan on the back, Yishui River in the East, and faces the village of Yanhui’s mother across the water. Nishan architectural complex is composed of temples in front and an academy in the back, each of which is an independent area. Having five courtyards and three routes layout, the temple covers an area of about 23 acres, with 27 buildings, 69 rooms and a construction area of 1700 square meters. In front of the temple is Zhiyuan River, across which a bridge is built.
In 2006, Nishan Mountain was announced as a national key cultural relics protection unit, and Nishan Confucian Temple and Academy were also listed as the expansion projects of the world cultural heritage of “Three Kong&rdquo.

Yan Temple(颜庙)
Yan Temple, also known as Fusheng temple, is a temple to worship Yan Hui, who is honored as Fusheng ( which means “another holy sage after Confucius”). Yan Hui, styled himself as Ziyuan, is a disciple of Confucius, known for his virtue, poor but studious, admired by later generations.The Major Scenic Spots include the residential area, the Well in the Rough Alley and the Fusheng Hall. Yan Temple is now a national key cultural relics protection unit.
Zhougong Temple(周公庙)
Zhougong Temple (the Temple of Duke Zhou), is the former Taimiao of the State of Lu. Taimiao is supposed to be the ancestral temple of the emperor. As Duke Zhou was only a vassal of the Zhou Dynasty, not the emperor, the Zhougong Temple should not have been called Taimiao. But Duke Zhou was with great achievements for creating rites and music, therefore King Cheng of Zhou specially authorized the State of Lu(Duke Zhou’s territory)to sacrifice the former emperor. As a result, the rites and music belonged to the emperor were practiced in the State of Lu. King Cheng ordered the Lu State to set up the Taimiao Temple after Duke Zhou's death.When the Lu State was destroyed by the Chu State, the Taimiao Temple also perished. Afterwards, the present Zhougong Temple were built and expanded six times in the Song, Yuan, Ming and Qing Dynasties, forming its current scale. It is said that the original site of the Taimiao Temple is where the present Zhougong Temple locates.
There are 57 halls, pavilions, gates, and residential area in three courtyards front and back (excluding the collapsed parts in the east and west courtyards), with a total area of 42 acres. Zhougong Temple is now a national key cultural relics protection unit.
尼山圣境
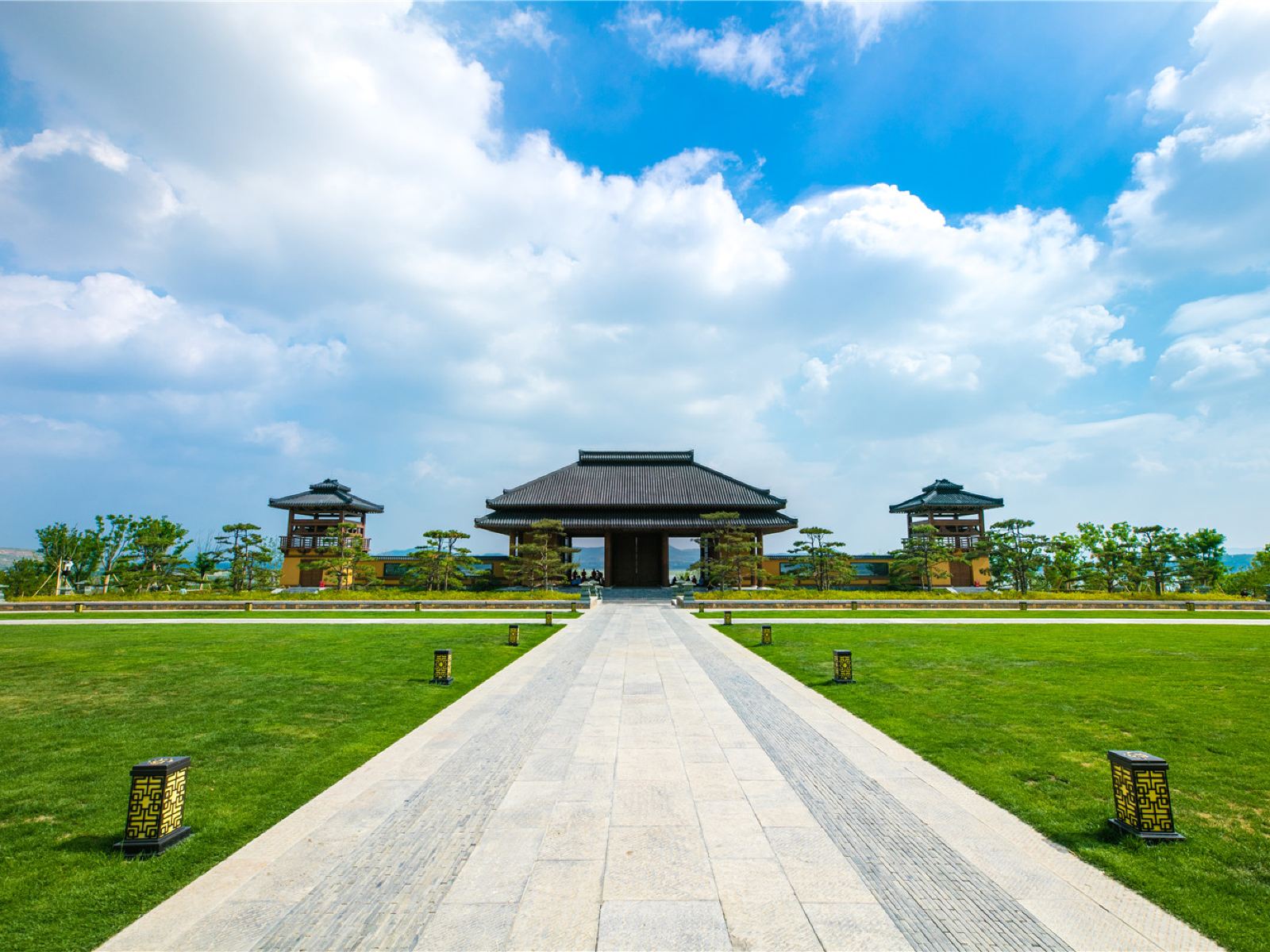
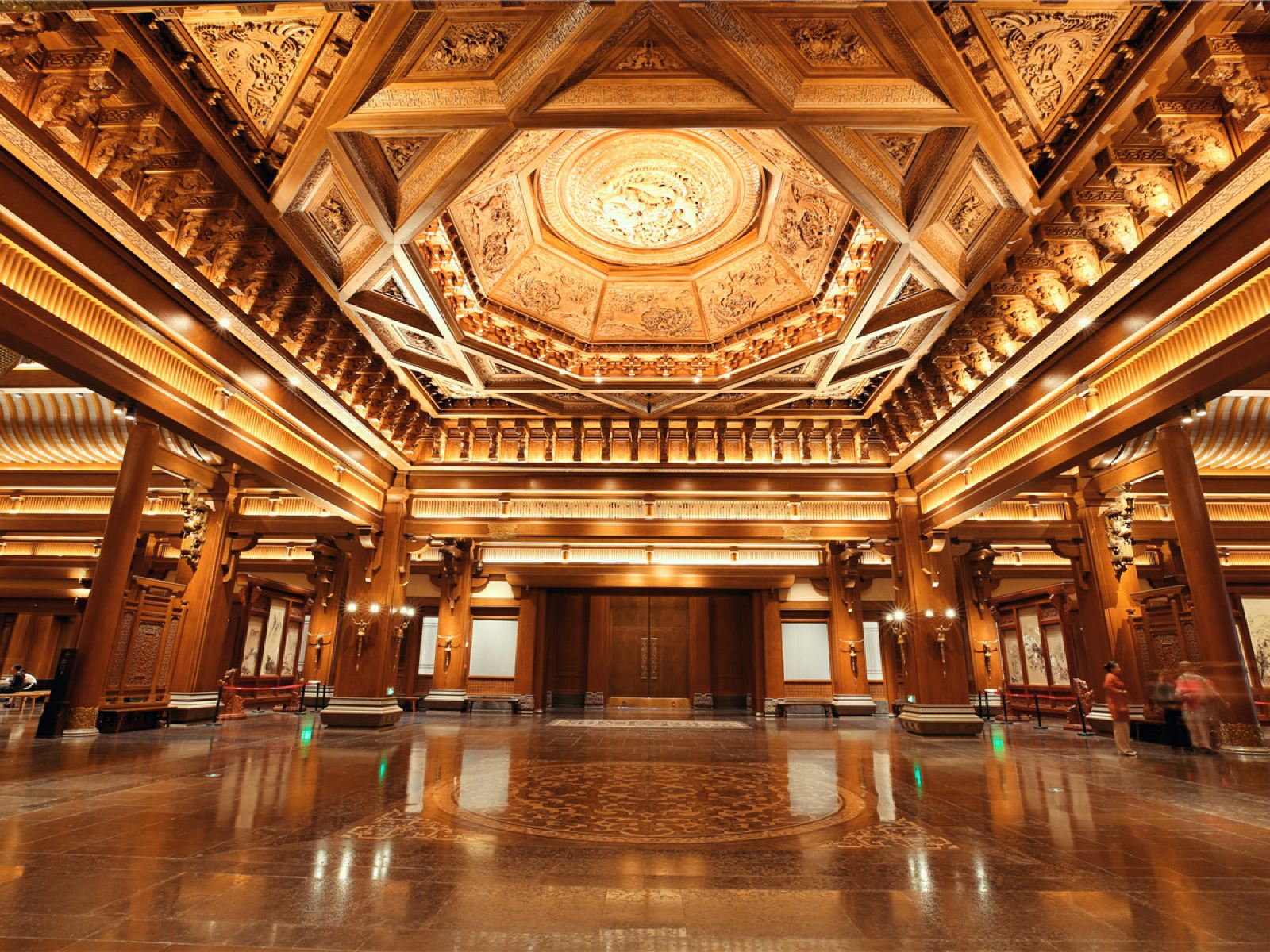






Some of the pictures are obtained from the network
please inform us if there is infringement
please inform us if there is infringement
SUBMISSION
 REGISTRATION
REGISTRATION
CONFERENCE INFORMATION
SHARE THIS CONFERENCE
VISITORS
SEARCH
- ICOCN'2022 in Shenzhen
- ICOCN'2021 Online
- ICOCN'2019 in Huangshan
- ICOCN'2018 in Zhuhai
- ICOCN'2017 in Wuzhen
- ICOCN'2016 in Hangzhou
- ICOCN'2015 in Nanjing
- ICOCN'2014 in Suzhou
- ICOCN'2013 in Chengdu
- ICOCN'2012 in Pattaya
- ICOCN'2011 in Guangzhou
- ICOCN'2010 in Nanjing
- ICOCN'2009 in Beijing
- ICOCN'2008 in Singapore
- ICOCN'2007 in Taxila
- ICOCN'2006 in Jiuzhaigou
- ICOCN'2005 in Bangkok
- ICOCN'2004 in Hong Kong
- ICOCN'2003 in Bangalore
- ICOCN'2002 in Singapore



